
“Specified Skilled worker(特定技能)” is a status of residence that is often associated with the idea that family members are not allowed to accompany or stay with the worker. Basically, “Specified Skilled Worker 1(特定技能1号)” does not allow family members to accompany or stay with the worker. On the other hand, “Specified Skilled worker 2(特定技能2号)” allows foreign nationals to bring their family members from their home countries or to support their spouses in case of marriage between foreigners in Japan. However, even if you are a “Specified Skilled Worker 1”, you may be allowed to have a family member reside in Japan as a dependent. This is the case where you and your family members were family members before you became Specified Skilled Workers.
This part will explain when a family member can be accompanied.
Family members may be allowed to accompany and stay in Japan even for Specified Skilled workers
The conditions for bringing and supporting family members vary between Specified Skilled Worker 1 and 2. Specified Skilled Worker 1 is basically not allowed to bring a family member, and the number of cases in which it is allowed is limited.
Specified Skilled Worker 1 on a case-by-case basis
In the case of Specified Skilled Worker 1, it is basically not allowed to bring a family member. However, under certain conditions, it may be permitted. For example, if a family member has already resided in Japan as a family member, they may be allowed to stay in Japan.
When family members are allowed to accompany and stay with the worker
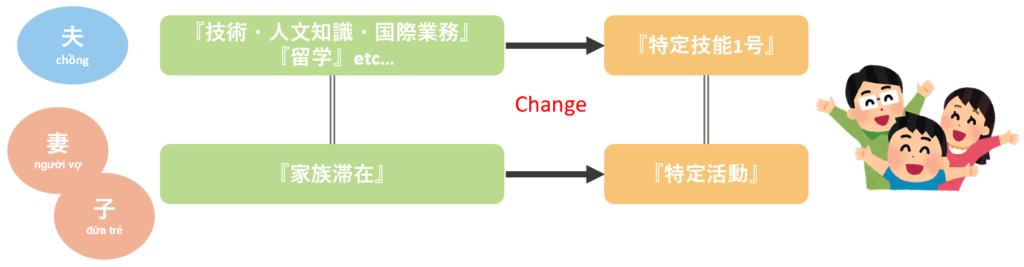
The following cases fall under the category of cases in which family members are allowed to accompany.
・Spouse or child of a mid-term resident whose status(身分) had already been established prior to the mid-term resident’s change of status to Specially Skilled Worker 1.
Specified Skilled Worker Screening Guidelines
・A child born to a Specified Skilled worker couple
In other words, the case applies to those who have been residing in Japan before becoming a Specified Skilled Worker and whose family members have already been residing in Japan as well. For example, if a couple has been residing in Japan under the status of “Dependent(家族滞在)”, “Student(留学)”, or “Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services(技術・人文知識・国際業務)”, and the spouse’s status of residence is changed when the supporter becomes a Specified Skilled Worker, etc., this can be the case.
In addition, children born to a couple who both work as Specified Skilled Worker foreigners are also permitted to accompany them.
In this case, “Designated Activities (Specified activities other than notifications)(特定活動(告示外特定活動))” will be granted. (*The status of residence is not “Dependent.”)
In addition, the applicant will be checked to ensure that he/she meets the requirements to be able to stay in Japan as a dependent without any problems, such as marital status and the ability of the supporter to support his/her family. Please refer to the next section for the points to be checked.
▶Reference:Q&A on the Specified Skilled Worker System 「Q9 Reference: Q&A on the Specified Skilled Worker System “Q9: If I am permitted to change my status from “Student” to “Specified Skilled Worker,” what will happen to my wife and children’s status of residence “Dependent”?」
When family members are not allowed to accompany or stay in Japan
On the other hand, if you get married after becoming a Specified Skilled Worker, your family members cannot be changed to “Designated Activities” or invited to Japan as family members. Even if your family relationship was established before you became a Specified Skilled Worker, you cannot invite your family to stay in Japan if they were not in Japan by the time you changed your status to Specified Skilled Worker.
In the case of Specified Skilled Worker 2, “Dependent” is allowed
In the case of “Specified Skilled Worker 2” status, family members are allowed to accompany and stay in Japan. In such a case, the status of residence is different from Specified Skilled Worker 1, and is recognized under the status of residence “Dependent”.
In the case of “Specified Skilled Worker 2” status, you are allowed to accompany and stay with your family members even if they are in your home country or you got married after you became a Specified Skilled Worker.
Scope of family members who can obtain “Dependent” status
The “spouse (wife/husband)” and “children” can be invited to Japan.
The spouse must be still married. Divorced or deceased spouses are not included. Also, a common-law spouse is not recognized. “Children” includes adopted children (both regular and specially adopted children). Children born before marriage and children born shortly after marriage (illegitimate children(非嫡出子)) are also recognized as “children” if they are acknowledged. A child is also recognized even if he or she has reached the age of majority.
Three points of “Dependent” status
②Ability to support/receive support
③Living together (in the case of spouses)
When applying for a “Dependent” visa, the applicant must be married. A common-law marriage or engaged status is not acceptable. The marriage must be legally valid. In addition, the “Dependent” visa status requires the applicant to be supported by a worker with a work visa. In other words, the supporter must be “capable of providing support” and the spouse must be “willing to receive support and stay in that status”. In addition, it is preferable for the couple to live together in order to receive support as a married couple.
If these conditions are met, and it is determined that there is no problem with the family members staying together, the status of “Dependent” will be granted to the family members of Specified Skilled Worker 2 foreign nationals.
Procedures for Status of Residence for Family Members of Specially Skilled Worker 1 and 2
This section explains the procedures for status of residence for family members of foreign nationals residing in Japan under Specially Skilled Worker 1 and 2.
What is the status of residence for which you are applying?
As explained in the previous section, there are cases in which family members may or may not be allowed to accompany and stay with a Specified Skilled Worker. Also, the status of residence for family members differs depending on the “Specially Skilled Worker 1” and “Specially Skilled Worker 2” statuses. The following is a summary of the status of residence for which an application is made.
| Name of Status of Residence | Name of the “Status of Residence” for which you are applying | Conditions for eligibility to apply |
|---|---|---|
| Specially Skilled Worker 1 | Designated activities other than notifications | ・If the family relationship was established before the supporter became a Specified Skilled Worker ・A child born to a couple who are both Specified Skilled Worker foreigners |
| Specially Skilled Worker 2 | Dependent | ・No restrictions like Specified Skilled Worker 1 (As per the requirements for “Dependent” status of residence) |
Application for status of residence (visa)
There are certain people and timing for applying for Designated Activities and Dependent (applied by the spouse of a Specially Skilled Worker 1 or 2). Even if all family members are abroad, it is possible to call all family members by having the company to which the supporter plans to belong act as a representative.
When can I apply?
In the case of Specially Skilled Worker 1, the timing of the application should coincide with the change in status of the supporter to Specially Skilled Worker 1, or, since it is assumed that the spouse is already residing in Japan for a specific purpose, the application should be filed as soon as the purpose of residence ceases (for example, upon graduation from college after staying on a student visa).
In the case of Specified Skilled Worker 2, if a family member is in Japan, the process should be completed immediately after the marriage is consummated for a married couple or after the birth of a child for a child. If the family member is currently abroad, the change should be made after the marriage is consummated or the birth of the child, but before the family member enters Japan.
Incidentally, in the case of Specified Skilled Worker II, it is possible to apply even if the supporter is also abroad and all family members are entering Japan at the same time. Even if the supporter has not worked in Japan, if the supporter’s work visa has been approved and the expected income is expected to be sufficient to live on, permission will be granted.
Where is the application to be made?
Basically, the application should be made at the Immigration Service Agency that has jurisdiction over the applicant’s residence, or at the Immigration Service Agency that has jurisdiction over the location of the company that plans to accept the supporter if the supporter is still abroad and the family members are entering the country at the same time.
The following are the rules regarding where to apply.
The regional immigration office with jurisdiction over the planned place of residence or the location of the accepting organization
【Application for change of status of residence or application for permission for extension of period of stay(在留資格変更許可申請 or 在留期間更新許可申請)】
Regional immigration office with jurisdiction over the place of residence
| Regional Immigration Office | Area of jurisdiction of the |
|---|---|
| Sapporo Immigration and Residence Office | Hokkaido |
| Sendai Immigration Bureau | Miyagi, Fukushima, Yamagata, Iwate, Akita, Aomori |
| Tokyo Immigration Bureau | Tokyo, Kanagawa Prefecture (Yokohama Branch Office has jurisdiction), Saitama Prefecture, Chiba Prefecture, Ibaraki Prefecture, Tochigi Prefecture, Gunma, Yamanashi, Nagano, Niigata |
| Nagoya Immigration Bureau | Aichi, Mie, Shizuoka, Gifu, Fukui, Toyama, Ishikawa |
| Osaka Immigration Bureau | Osaka, Kyoto, Hyogo (Kobe Branch Office has jurisdiction), Nara, Shiga and Wakayama Prefectures |
| Hiroshima Immigration Bureau | Hiroshima, Yamaguchi, Okayama, Tottori, Shimane |
| Fukuoka Immigration Bureau | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Oita, Kumamoto, Kagoshima, Miyazaki Prefectures, Okinawa Prefecture (Naha Branch Office has jurisdiction) |
If there is no branch office nearby, you may apply at the nearest branch or local office. However, depending on the branch office, there may be cases where they do not accept applications for status of residence, so please check with them.
▶ Immigration Services Agency: Jurisdiction
Who makes the application?
Basically, the applicant (foreign national) himself/herself goes to the Immigration Service Agency with jurisdiction over the applicant’s place of residence to apply. If the applicant is a child under 16 years of age, a legal representative (such as a parent) may apply on his/her behalf.
If the family member whom the applicant wishes to call is abroad, the supporter can apply by going to the Immigration Service Agency with jurisdiction over the supporter’s place of residence. If both the applicant and the supporter are abroad, an official of the organization that intends to accept the supporter or other person designated by a Ministry of Justice ordinance(法務省令) is to file the application on behalf of the applicant.
An “Agent(取次者)” who has filed an application can file the application on behalf of the applicant.
Examples of “Agents” include employees of the organization to which they are employed or affiliated, administrative scrivener(行政書士), attorneys, and staff of registered support organizations(登録支援機関), but only those who have received certain training and are registered.
Conclusion
The above is an explanation of the requirements for family members who are dependent on a person residing under the “Specially Skilled Worker 1 or 2” visa status. In the case of “Specially Skilled Worker 1”, it is said that family members are basically not allowed to accompany the worker, but in certain cases, they may be allowed to stay in Japan. On the other hand, in the case of “Specified Skilled Worker 2”, family members are allowed to accompany the worker if they meet the requirements for the “Dependent” visa status, as is the case with other work visas.



