
If a parent is a “Permanent Resident”, his/her child will apply for “Permanent Resident”, “Long Term Resident(定住者)”, or “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident(永住者の配偶者等)” status of residence (visa). The status of residence (visa) that can be applied for depends on the situation. This section explains which status of residence (visa) a child of a “Permanent Resident” can apply for.
About the status of residence (visa) that the child of a “Permanent Resident” can apply for

There are three main types of status of residence that children of “Permanent Residents” can apply for: “Permanent Resident,” “Long Term Resident,” and “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident”. Each of these statuses has its own rules and precautions.
“Permanent Resident” (acquisition of permanent residence by birth)
This section explains when a child of a “Permanent Residents” can “acquire” the status of “Permanent Resident”.
Under what circumstances can an application be made?
*The same is true for cases where the parent is a Special Permanent Resident(特別永住者), but it is common for Special Permanent Residents to apply for a “Application for Special Permanent Residence ”(「特別永住許可申請」) at the municipal office.
Note that, the application must be filed within 30 days from the date of birth.
In addition, “child born in Japan” literally means a child born in Japan. Even if the mother is a person who normally resides in Japan and is leaving Japan under a re-entry permit (including special re-entry permit) to give birth in her home country, the child cannot apply for “Permanent Resident” status because he/she was not born in Japan. Also, If the family leaves the country after birth before obtaining “Permanent Resident” status, the child cannot apply for “Permanent Resident” status.
Point
If either the “father” or “mother” is a “Permanent Resident,” the child is eligible to apply. Also, please note that “30 days” from the date of birth is a short period of time, so it is advisable to understand the procedure before birth.
In addition, “Permanent Resident” is not granted by default. If “Permanent Resident” status is not granted, a status such as “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident” will be granted (if the requirements are met).
A child may not be allowed to obtain “Permanent Resident” status by birth if the parent is subject to grounds for deportation, if the supporter is a public burden, or if the parent has not paid taxes.
A child of a “Permanent Resident” who is residing in Japan with a status other than “Permanent Resident” (e.g., “Long Term Resident”) may apply for “Permanent Resident” status after residing in Japan for at least one year (there are other requirements that must be met).
Long Term Resident (if born outside of Japan)
To obtain Permanent Resident status, the child must be born in Japan. If the child was born outside of Japan, the applicant must apply for Long Term Resident status.
In what cases can an application be made?
Even if the child is a child of “Permanent Resident”, a child “born abroad” or “not continuously residing in Japan” do not apply for “Permanent Resident” but for “Long Term Resident” (Notification No. 6 (a)(告示6号イ)).
Point
A child born abroad must apply for “Application for Certificate of Eligibility”(「在留資格認定証明書交付申請」 )for Long Term Resident (Notification No. 6) before entering and staying in Japan. While receiving support from a “Permanent Resident” or other such status, the child may stay in Japan under this status until he/she becomes 18 years old.
There is an upper age limit for this status of residence. Children of Permanent Residents may apply for “Permanent Resident” status if they have been residing in Japan for more than one year, and we recommend that you change your status as soon as you meet the requirements.
Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident
A child can be a biological child or a recognized child, but not an adopted child.
If a “Permanent Resident” cannot be obtained, or especially if the application deadline has passed, the “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident” may be applied for. When 30 days have passed since the birth of a child of a “Permanent Resident” or when the application deadline for Application for Special Permanent Resident (within 60 days of birth) has passed for a child of a “Special Permanent Resident”, the acquisition of “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident” will be considered.
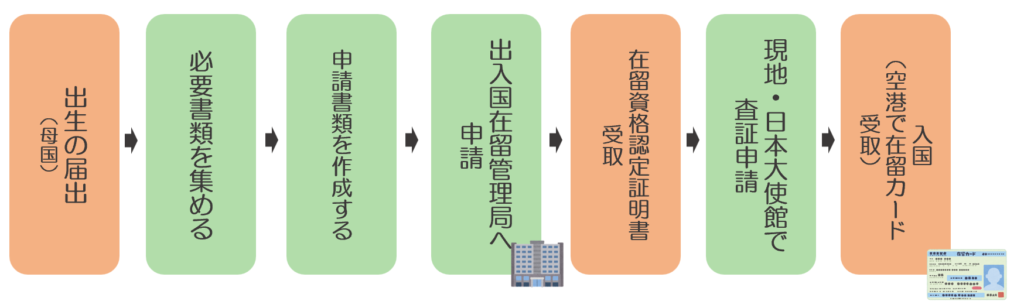
Steps to Apply for Status of Residence

A “Permanent Resident” or “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident” applies for a “Application for Permanent Residence “. If you wish to invite a child born abroad to Japan, you must apply for “Application for Certificate of Eligibility”. This section discusses these two examples.
In the case of acquiring “Permanent Resident” status
First, the necessary procedures must be taken from birth to application.
Procedures
- Submit a birth certificate at the municipal office within 14 days of birth.
- Report the birth to the home country and apply for a passport at the embassy or consulate.
- Apply for a “Application for Permanent Residence ” within 30 days of birth
While there are many things to do, such as reporting the birth at the city hall and applying for a passport at the consulate or embassy, you must also prepare well for the “Application for Permanent Residence”, which is a hard schedule.
The application is filed at the Immigration Service Agency that has jurisdiction over the Permanent Resident’s (parent’s) place of residence.
Required Documents for “Application for Permanent Residence”
| acquisition of permanent residence by birth |
|---|
| ・Permanent residence application form(永住許可申請書) ・Birth certificate ・Resident card (住民票) ・Certificate of Employment(在職証明書) or materials that certify the occupation of the Permanent Resident(supporter, parents) ・ Documents certifying the most recent (past 1 year) income and tax payment status of the Permanent Resident(supporter, parents) ⇒taxation certificate of residence tax(住民税の課税証明書), tax payment certificate(納税証明書), and tax payment certificate issued by the tax office(no.3) ・Documents certifying the payment status of public pension and public medical insurance premiums of the Permanent Resident (supporter, parents) ・ A Health insurance card (copy)(健康保険証の写し)of Permanent Resident(supporter, parents) ,and their child ・Letters of guarantee(身元保証書) ・Documents that certify the identity of the guarantor(身元保証人の身分証明書) ・Questionnaire(質問書) |
*In addition to the above, documents may also be submitted to explain income and the fulfillment of official obligations. The above information is the minimum required documentation.
When applying for “Long Term Resident” (when considering bringing in your child from abroad)
Procedures
The procedure for inviting a Permanent Resident’s child born overseas to Japan is called an “Application for Certificate of Eligibility(「在留資格認定証明書交付申請」).This procedure is carried out at the Immigration Service Agency, by the person (Permanent Resident) calling the child acting as his/her representative.
Required Documents for “Long Term Resident (Notification No. 6, a)”
| Application for Certificate of Eligibility |
|---|
| ・Application form for Certificate of Eligibility(在留資格認定証明書交付申請書) ・ID Photo ・Birth certificate ・Certificate of Employment(在職証明書) or materials that certify the occupation of the Permanent Resident(supporter) ・Permanent resident (supporter)taxation certificate of residence tax and tax payment certificate for the most recent year ・Permanent resident’s (supporter’s)Resident card ・Letters of guarantee |
*In addition to the above, documents may also be submitted to explain income and the fulfillment of official obligations. The above information is the minimum required documentation.
【Supplementary Information】 What about Japanese’s children?

If the father or mother is Japanese at the time of birth, the child becomes a “Japanese citizen”. If the child has “Japanese nationality”, he/she is not a foreigner and does not need to have a status of residence in order to live in Japan.
Article 2 A child is a Japanese citizen in the following cases:
Nationality Act(国籍法) article 2
(i)if the father or mother is a Japanese citizen at the time of birth;
(ii)if the father died before the child’s birth and was a Japanese citizen at the time of death; or
(iii)if born in Japan and both of the parents are unknown or are without nationality.
In the case of a “Japanese” child born abroad, a “notification of reservation of nationality” is made. By doing so, the child can maintain his/her Japanese nationality. If a child has dual nationality, he/she is required to choose a nationality by the age of 18. Under Japan’s Nationality Act, “choosing a foreign nationality” automatically results in the loss of Japanese nationality.
Even if a child’s father or mother is a Japanese citizen at the time of birth, if the child subsequently chooses to become a foreign citizen, he or she will become a foreigner and will need “status of residence” in order to live in Japan. Since the status of residence that can be applied for changes depending on the situation at that time, it is necessary to apply for the appropriate status of residence.
Conclusion
The above is an explanation of the status of residence (visa) that a child of a “Permanent Resident” can apply for.
If the parent is a “Permanent Resident” and the child was born in Japan, the child can apply for Permanent Resident within 30 days. In the case of a child born abroad, the child must apply for “Long Term Resident” status, not “Permanent Resident” or “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident” status.


